Overview of SAP MM Module
What is SAP
SAP is a Enterprise resource planning (ERP) software owned by SAP Germany.
SAP stands for systems Applications and Products in data processing
SAP has various modules like MM, SD, FI, HR, PM, PS, PP, QM which are linked to each other
SAP is a Enterprise resource planning (ERP) software owned by SAP Germany.
SAP stands for systems Applications and Products in data processing
SAP has various modules like MM, SD, FI, HR, PM, PS, PP, QM which are linked to each other
Overview of SAP MM Module
• Processes in Procurement
• Inventory management and physical
inventory
• Pricing in Purchasing
• Invoice verification
Topic 1: Processes in Procurement
• Basics of Procurement
• Master data
• Procurement of Stock Material
• Procurement of Consumable
material
• Procurement of External services
• Contracts and Scheduling
agreements
• Document Release procedure
Topic 2: Inventory management and
Physical inventory
• Goods receipt
• Stock transfers and Transfer
postings
• Reservations
• Goods issues
• Special stocks as below two types
Sub
contracting
Vendor Consignment
• Material valuation and split
valuation
• Physical inventory and cycle
counting
• Movement types
Topic 3: Pricing in Purchasing
• Conditions in purchasing
Access sequence, condition types and
Pricing schema (pricing procedure)
• Price determination
How is price determined in PO
• Customizing pricing
Create condition tables, access
sequence, condition types and pricing procedure
Topic 4: Invoice verification
• Basics of invoice verification
• Taxes cash discounts and foreign
currency
• Variances and invoice blocking
• Invoices for POs with Account
assignment
• Delivery costs
• Invoices without reference to POs
• Credit memos
• Invoice parking
• Automatic settlements
Basics of
Procurement
In Basics
of Procurement we will study about below sub topics
• Organizational Structure
• Types of Purchasing organization
• Procurement cycle – Creation of
purchase order to invoice verification
Organizational Structure in SAP
MM
Organizational Structure in SAP
MM
• Client is the organizational unit
within the R/3 system with its own data, master records and set of tables. In
business perspective client forms a corporate group.
• Company Code is the central organizational
unit of financial accounting. A company has its own balance sheet.
• Plant is a organizational unit where
production, procurement, plant maintenance and material planning is carried
out.
• Storage location is a organizational unit within a plant that
allows differentiation of stocks.
• Purchasing organization and
Purchasing group
A
purchasing organization negotiates conditions of purchase with vendors for one
or more plants.
A purchasing group is a buyer or a
group of Buyers responsible for certain purchasing activities.
Types of Purchasing Organizations
• Plant specific purchase
organization
Here the purchasing organization
is responsible for procuring materials for one plant only.
• Cross plant purchasing
organization
A
cross plant purchasing organization is set up for each company code. This
purchasing organization procures materials for all plants assigned to the
company code.
• Cross company code purchasing
organization
In
a cross company code purchasing organization, we cannot assign a company code
to purchasing organization in customizing.
In
this case when we create a PO the systems asks to enter the company code for
which we have to procure materials.
Plant
specific purchasing organization
In plant-specific procurement, a purchasing organization is responsible for procuring materials for one plant only.
In plant-specific procurement, a purchasing organization is responsible for procuring materials for one plant only.
Cross
plant purchasing organization
A cross plant purchasing organization is set up for each company code. This purchasing organization procures materials for all plants assigned to the company code.
A cross plant purchasing organization is set up for each company code. This purchasing organization procures materials for all plants assigned to the company code.
Cross
company code purchasing organization
In a cross company code purchasing organization, we cannot assign a company code to purchasing organization in customizing.
In this case when we create a PO the systems asks to enter the company code for which we have to procure materials.
In a cross company code purchasing organization, we cannot assign a company code to purchasing organization in customizing.
In this case when we create a PO the systems asks to enter the company code for which we have to procure materials.
Procurement
cycle
Procurement cycle consists of below steps
Procurement cycle consists of below steps
• Determination of requirements: The user department creates a PR
for a material and passes it to purchasing department. If we have set up a MRP
procedure for a material in the material master the R/3 system automatically
generates a PR.
• Determination of source of
supply: The buyer determines the sources
of supply. If there is a vendor for the material then a PO is raised by Buyer.
If there is no source the buyer raises request for quotation (RFQ) and sends to
possible sources.
• Vendor selection:
The system
compares the prices of various quotations and automatically sends rejection
letters (to high price quotations) and selects the vendor with least price.
• Purchase order processing: When we are entering PO’s the
system provides data like
material PO text price etc. PO is created and sent to vendor.
• Purchase order monitoring:
The buyer
monitors the status of PO at any time and checks if goods or invoice has been
received for the PO item/items. If goods are not received system sends reminder
letters automatically.
• Goods Receipt:
When the goods
are received in stores the system compares the goods receipt qty with PO qty
and posts GR.
• Invoice verification:
After goods
receipt is done the vendor invoices are checked for accuracy of prices and
other contents and invoice is posted.
• Payment processing:
Financial
accounting deals with payments. Payment is done to vendor by Finance
department.
Purchase
Requisition
• PR’s are created manually by user
or automatically by system by MRP procedure.
• When PR is created for materials
with material master record the system captures the data from material master
record into the PR. The purchasing dept. converts the PR into RFQ, PO or
outline agreement.
RFQ/Quotation
• The buyer can enter RFQ manually
or automatically. The RFQ is
sent to suitable vendors whose
address is taken from vendor master records.
• The vendors will send their
quotations or rejection letters. The buyer enters the conditions, price &
delivery dates of quotations in the system.
• The system compares the
quotations and finds the most favorable vendor.
Purchase
order
• A PO is a request to a vendor to
supply certain goods or services under stated conditions.
• A PO can be created without
reference, w.r.t a PR, RFQ or another PO.
• When we enter PO data the system
suggests ordering address, terms of payment and incoterms from vendor master
record, material text from material master record and price from purchasing
information records. The PO is sent to vendor
Goods
receipt
• The goods receiving dept. will
check the quantity & quality of item received w.r.t PO. When we post goods receipt the system creates
a material document (GRS).
• The system also creates one
accounting document which records the
effect of goods movement on value of stock.
• The PO history is automatically
updated in the system.
Invoice
processing
• When we enter a invoice w.r.t a
PO the system suggests data from PO and goods receipt for PO. (For data like
vendor material, qty, terms of payment etc).
• If there are discrepancies
between PO, goods receipt and invoice the system blocks the invoice for
payment.
• If the invoice is O.K. the system
posts the invoice and financial accounting dept makes payment to vendor.
Exercise
- Create a Purchase order, Post Goods receipt and Post Invoice
Create
Purchase order ME21N
Change
Purchase order ME22N
Display
Purchase order ME23N
Vendor –
245
Purchasing
org – 1111
Purchasing
group – 001
Company
code – 1111
Material
– 3424
Qty – 10
Price –
11
Delivery
date - Today
Plant –
1111
Storage
loc – 1111
Tax code
GX
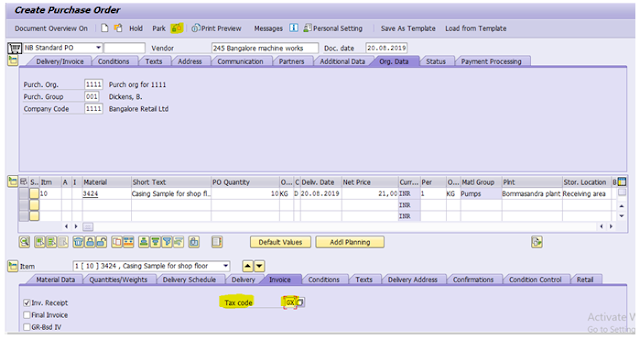
ME21N
Input
the data as shown highlighted in yellow
Press
Enter
In the
invoice tab page input Tax code GX
Click
Check button
We get
message “No messages issued during check”
Click
Save
Exercise: Post Goods Receipt for
Purchase order
Transaction
code – MIGO
PO
number – previously created PO
Plant –
1111, movement type – 101
Date –
Today, Delivery Note – REF-1555
Qty
received – 10 Pc
Check
Item OK
Click
Check and Post
Note
down the material document number created
Go to ME23N
PO display and in PO history tab page we can see the material document number
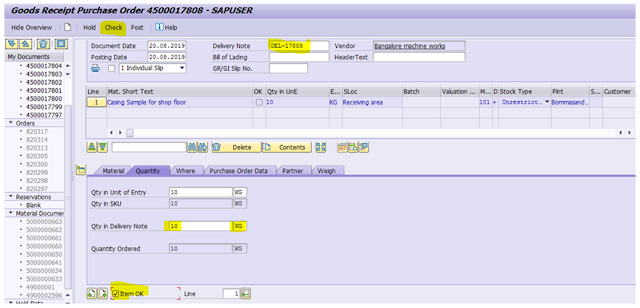
MIGO
Select Goods Receipt and Purchase order
Input the previously created PO 4500017808, Plant 1111, GR
Goods Receipt 101 movement type
Input Delivery # DEL-17808
Qty in Delivery Note 10 KG
Check Item OK
Click Check button at top
We get message Document is OK
Click Post button at top
Material Document number – 5000000670
Display the material document in PO history
ME23N
Exercise: Post Invoice for the Purchase order
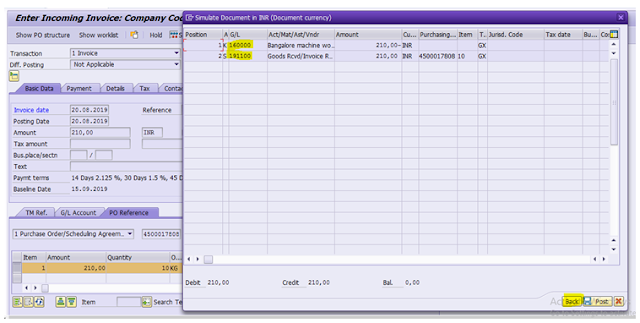
MIRO
Select Invoice
I put Invoice date – Today
Rreference – Our PO number
In PO Reference tab page select Purchase order/Scheduling
Agreement
Input PO # 4500017808
Also select Goods/service items + planned delivery costs
Enter
In next screen above we will see Balance as 210 Rs which is
equal to PO amount 210 Rs
Input this in Invoice Amount field in Basic Data tab
Enter
The Balance field becomes green which means the invoice
amount is correct
Click Simulate button at top
A new pop up window will open and we can see the G/L Accounts
to which the amount is posted
Click Back
Save
Invoive no 5105609252 created
Display Invoice in PO history
ME23N
In Purchase Order History tab in Item details, we can see the
Invoice document number





















No comments:
Post a Comment